1. Collection接口概述
-
JDK不提供此接口的任何直接实现,而是提供更具体的子接口(如:Set和List)去实现。
-
Collection 接口是 List和Set接口的父接口,该接口里定义的方法既可用于操作 Set 集合,也可用于操作 List 集合。方法如下:
2. 添加
(1)add(E obj):添加元素对象到当前集合中
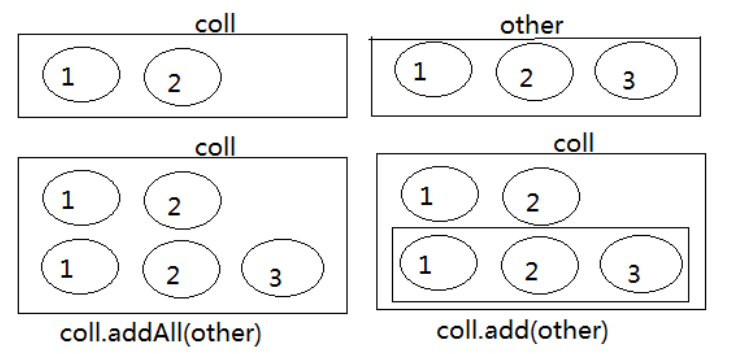
(2)addAll(Collection other):添加other集合中的所有元素对象到当前集合中,即this = this ∪ other
注意:add和addAll的区别
package com.atguigu.collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class TestCollectionAdd {
@Test
public void testAdd(){
//ArrayList是Collection的子接口List的实现类之一。
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("小李广");
coll.add("扫地僧");
coll.add("石破天");
System.out.println(coll);
}
@Test
public void testAddAll(){
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
c1.add(1);
c1.add(2);
System.out.println("c1集合元素的个数:" + c1.size());//2
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
c2.add(1);
c2.add(2);
System.out.println("c2集合元素的个数:" + c2.size());//2
System.out.println("c2 = " + c2);
Collection other = new ArrayList();
other.add(1);
other.add(2);
other.add(3);
System.out.println("other集合元素的个数:" + other.size());//3
System.out.println("other = " + other);
System.out.println();
c1.addAll(other);
System.out.println("c1集合元素的个数:" + c1.size());//5
System.out.println("c1.addAll(other) = " + c1);
c2.add(other);
System.out.println("c2集合元素的个数:" + c2.size());//3
System.out.println("c2.add(other) = " + c2);
}
}
注意:coll.addAll(other);与coll.add(other);
3. 判断
(3)int size():获取当前集合中实际存储的元素个数
(4)boolean isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空集合
(5)boolean contains(Object obj):判断当前集合中是否存在一个与obj对象equals返回true的元素
(6)boolean containsAll(Collection coll):判断coll集合中的元素是否在当前集合中都存在。即coll集合是否是当前集合的“子集”
(7)boolean equals(Object obj):判断当前集合与obj是否相等
package com.atguigu.collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
public class TestCollectionContains {
@Test
public void test01() {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
System.out.println("coll在添加元素之前,isEmpty = " + coll.isEmpty());
coll.add("小李广");
coll.add("扫地僧");
coll.add("石破天");
coll.add("佛地魔");
System.out.println("coll的元素个数" + coll.size());
System.out.println("coll在添加元素之后,isEmpty = " + coll.isEmpty());
}
@Test
public void test02() {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("小李广");
coll.add("扫地僧");
coll.add("石破天");
coll.add("佛地魔");
System.out.println("coll = " + coll);
System.out.println("coll是否包含“小李广” = " + coll.contains("小李广"));
System.out.println("coll是否包含“宋红康” = " + coll.contains("宋红康"));
Collection other = new ArrayList();
other.add("小李广");
other.add("扫地僧");
other.add("尚硅谷");
System.out.println("other = " + other);
System.out.println("coll.containsAll(other) = " + coll.containsAll(other));
}
@Test
public void test03(){
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
c1.add(1);
c1.add(2);
System.out.println("c1集合元素的个数:" + c1.size());//2
System.out.println("c1 = " + c1);
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
c2.add(1);
c2.add(2);
System.out.println("c2集合元素的个数:" + c2.size());//2
System.out.println("c2 = " + c2);
Collection other = new ArrayList();
other.add(1);
other.add(2);
other.add(3);
System.out.println("other集合元素的个数:" + other.size());//3
System.out.println("other = " + other);
System.out.println();
c1.addAll(other);
System.out.println("c1集合元素的个数:" + c1.size());//5
System.out.println("c1.addAll(other) = " + c1);
System.out.println("c1.contains(other) = " + c1.contains(other));
System.out.println("c1.containsAll(other) = " + c1.containsAll(other));
System.out.println();
c2.add(other);
System.out.println("c2集合元素的个数:" + c2.size());
System.out.println("c2.add(other) = " + c2);
System.out.println("c2.contains(other) = " + c2.contains(other));
System.out.println("c2.containsAll(other) = " + c2.containsAll(other));
}
}
4. 删除
(8)void clear():清空集合元素
(9) boolean remove(Object obj) :从当前集合中删除第一个找到的与obj对象equals返回true的元素。
(10)boolean removeAll(Collection coll):从当前集合中删除所有与coll集合中相同的元素。即this = this – this ∩ coll
(11)boolean retainAll(Collection coll):从当前集合中删除两个集合中不同的元素,使得当前集合仅保留与coll集合中的元素相同的元素,即当前集合中仅保留两个集合的交集,即this = this ∩ coll;
注意几种删除方法的区别
package com.atguigu.collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class TestCollectionRemove {
@Test
public void test01(){
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("小李广");
coll.add("扫地僧");
coll.add("石破天");
coll.add("佛地魔");
System.out.println("coll = " + coll);
coll.remove("小李广");
System.out.println("删除元素\"小李广\"之后coll = " + coll);
coll.clear();
System.out.println("coll清空之后,coll = " + coll);
}
@Test
public void test02() {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("小李广");
coll.add("扫地僧");
coll.add("石破天");
coll.add("佛地魔");
System.out.println("coll = " + coll);
Collection other = new ArrayList();
other.add("小李广");
other.add("扫地僧");
other.add("尚硅谷");
System.out.println("other = " + other);
coll.removeAll(other);
System.out.println("coll.removeAll(other)之后,coll = " + coll);
System.out.println("coll.removeAll(other)之后,other = " + other);
}
@Test
public void test03() {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("小李广");
coll.add("扫地僧");
coll.add("石破天");
coll.add("佛地魔");
System.out.println("coll = " + coll);
Collection other = new ArrayList();
other.add("小李广");
other.add("扫地僧");
other.add("尚硅谷");
System.out.println("other = " + other);
coll.retainAll(other);
System.out.println("coll.retainAll(other)之后,coll = " + coll);
System.out.println("coll.retainAll(other)之后,other = " + other);
}
}
5. 其它
(12)Object[] toArray():返回包含当前集合中所有元素的数组
(13)hashCode():获取集合对象的哈希值
(14)iterator():返回迭代器对象,用于集合遍历
public class TestCollectionContains {
@Test
public void test01() {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("小李广");
coll.add("扫地僧");
coll.add("石破天");
coll.add("佛地魔");
//集合转换为数组:集合的toArray()方法
Object[] objects = coll.toArray();
System.out.println("用数组返回coll中所有元素:" + Arrays.toString(objects));
//对应的,数组转换为集合:调用Arrays的asList(Object ...objs)
Object[] arr1 = new Object[]{123,"AA","CC"};
Collection list = Arrays.asList(arr1);
System.out.println(list);
}
}