1. 常用方法
Collections 中提供了一系列静态的方法对集合元素进行排序、查询和修改等操作,还提供了对集合对象设置不可变、对集合对象实现同步控制等方法(均为static方法):
排序操作:
-
reverse(List):反转 List 中元素的顺序
-
shuffle(List):对 List 集合元素进行随机排序
-
sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序
-
sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序
-
swap(List,int, int):将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换
查找
-
Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
-
Object max(Collection,Comparator):根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
-
Object min(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素
-
Object min(Collection,Comparator):根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素
-
int binarySearch(List list,T key)在List集合中查找某个元素的下标,但是List的元素必须是T或T的子类对象,而且必须是可比较大小的,即支持自然排序的。而且集合也事先必须是有序的,否则结果不确定。
-
int binarySearch(List list,T key,Comparator c)在List集合中查找某个元素的下标,但是List的元素必须是T或T的子类对象,而且集合也事先必须是按照c比较器规则进行排序过的,否则结果不确定。
-
int frequency(Collection c,Object o):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数
复制、替换
-
void copy(List dest,List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中
-
boolean replaceAll(List list,Object oldVal,Object newVal):使用新值替换 List 对象的所有旧值
-
提供了多个unmodifiableXxx()方法,该方法返回指定 Xxx的不可修改的视图。
添加
- boolean addAll(Collection c,T… elements)将所有指定元素添加到指定 collection 中。
同步
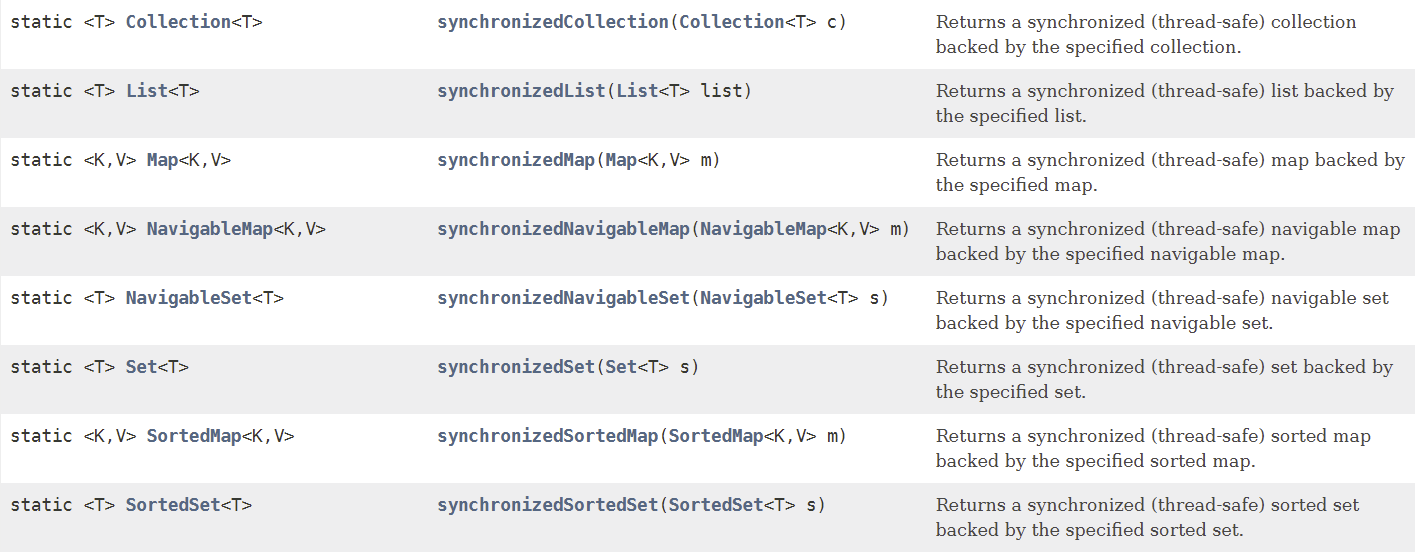
- Collections 类中提供了多个 synchronizedXxx() 方法,该方法可使将指定集合包装成线程同步的集合,从而可以解决多线程并发访问集合时的线程安全问题:
2. 举例
package com.atguigu.collections;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.text.Collator;
import java.util.*;
public class TestCollections {
@Test
public void test01(){
/*
public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> c,T... elements)
将所有指定元素添加到指定 collection 中。Collection的集合的元素类型必须>=T类型
*/
Collection<Object> coll = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coll, "hello","java");
Collections.addAll(coll, 1,2,3,4);
Collection<String> coll2 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coll2, "hello","java");
//Collections.addAll(coll2, 1,2,3,4);//String和Integer之间没有父子类关系
}
@Test
public void test02(){
/*
* public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll)
* 在coll集合中找出最大的元素,集合中的对象必须是T或T的子类对象,而且支持自然排序
*
* public static <T> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll,Comparator<? super T> comp)
* 在coll集合中找出最大的元素,集合中的对象必须是T或T的子类对象,按照比较器comp找出最大者
*
*/
List<Man> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Man("张三",23));
list.add(new Man("李四",24));
list.add(new Man("王五",25));
/*
* Man max = Collections.max(list);//要求Man实现Comparable接口,或者父类实现
* System.out.println(max);
*/
Man max = Collections.max(list, new Comparator<Man>() {
@Override
public int compare(Man o1, Man o2) {
return o2.getAge()-o2.getAge();
}
});
System.out.println(max);
}
@Test
public void test03(){
/*
* public static void reverse(List<?> list)
* 反转指定列表List中元素的顺序。
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world");
System.out.println(list);
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test04(){
/*
* public static void shuffle(List<?> list)
* List 集合元素进行随机排序,类似洗牌,打乱顺序
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world");
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test05() {
/*
* public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list)
* 根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序
*
* public static <T> void sort(List<T> list,Comparator<? super T> c)
* 根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序
*/
List<Man> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Man("张三",23));
list.add(new Man("李四",24));
list.add(new Man("王五",25));
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Man>() {
@Override
public int compare(Man o1, Man o2) {
return Collator.getInstance(Locale.CHINA).compare(o1.getName(),o2.getName());
}
});
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test06(){
/*
* public static void swap(List<?> list,int i,int j)
* 将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world");
Collections.swap(list,0,2);
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test07(){
/*
* public static int frequency(Collection<?> c,Object o)
* 返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world","hello","hello");
int count = Collections.frequency(list, "hello");
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}
@Test
public void test08(){
/*
* public static <T> void copy(List<? super T> dest,List<? extends T> src)
* 将src中的内容复制到dest中
*/
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++){//1-5
list.add(i);
}
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=11; i<=13; i++){//11-13
list2.add(i);
}
Collections.copy(list, list2);
System.out.println(list);
List<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=11; i<=20; i++){//11-20
list3.add(i);
}
//java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Source does not fit in dest
//Collections.copy(list, list3);
//System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test09(){
/*
* public static <T> boolean replaceAll(List<T> list,T oldVal,T newVal)
* 使用新值替换 List 对象的所有旧值
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world","hello","hello");
Collections.replaceAll(list, "hello","song");
System.out.println(list);
}
}
3. 练习
练习:
请从键盘随机输入10个整数保存到List中,并按倒序、从大到小的顺序显示出来
**练习2:**模拟斗地主洗牌和发牌,牌没有排序
效果演示:

提示:
String[] num = {"A","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10","J","Q","K"};
String[] color = {"方片","梅花","红桃","黑桃"};
ArrayList<String> poker = new ArrayList<>();
代码示例:
public class PokerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] num = {"A","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10","J","Q","K"};
String[] color = {"方片","梅花","红桃","黑桃"};
ArrayList poker = new ArrayList();
//1. 生成54张扑克牌
for (String s1 : color) {
for (String s2 : num) {
poker.add(s1.concat(" " + s2));
}
}
poker.add("小王");
poker.add("大王");
//2. 洗牌
Collections.shuffle(poker);
//3. 发牌
ArrayList tomCards = new ArrayList();
ArrayList jerryCards = new ArrayList();
ArrayList meCards = new ArrayList();
ArrayList lastCards = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < poker.size(); i++) {
if(i >= poker.size() - 3){
lastCards.add(poker.get(i));
}else if(i % 3 == 0){
tomCards.add(poker.get(i));
}else if(i % 3 == 1){
jerryCards.add(poker.get(i));
}else {
meCards.add(poker.get(i));
}
}
//4. 看牌
System.out.println("Tom:\n" + tomCards);
System.out.println("Jerry:\n" + jerryCards);
System.out.println("me:\n" + meCards);
System.out.println("底牌:\n" + lastCards);
}
}