-
为了提高数据读写的速度,Java API提供了带缓冲功能的流类:缓冲流。 -
缓冲流要“套接”在相应的节点流之上,根据数据操作单位可以把缓冲流分为:
-
字节缓冲流:
BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream -
字符缓冲流:
BufferedReader,BufferedWriter
-
-
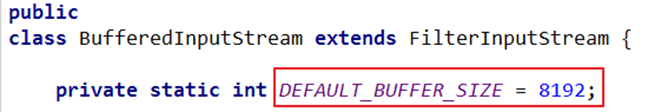
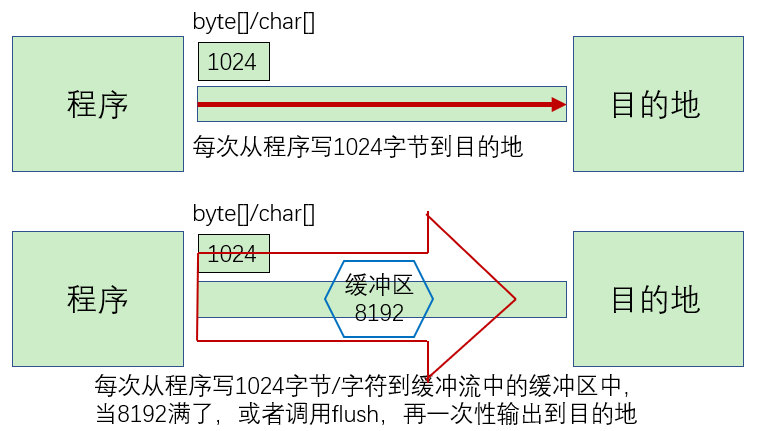
缓冲流的基本原理:在创建流对象时,内部会创建一个缓冲区数组(缺省使用
8192个字节(8Kb)的缓冲区),通过缓冲区读写,减少系统IO次数,从而提高读写的效率。
1. 构造器
-
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in):创建一个 新的字节型的缓冲输入流。 -
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out): 创建一个新的字节型的缓冲输出流。
代码举例:
// 创建字节缓冲输入流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("abc.jpg"));
// 创建字节缓冲输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("abc_copy.jpg"));
-
public BufferedReader(Reader in):创建一个 新的字符型的缓冲输入流。 -
public BufferedWriter(Writer out): 创建一个新的字符型的缓冲输出流。
代码举例:
// 创建字符缓冲输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("br.txt"));
// 创建字符缓冲输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("bw.txt"));
2. 效率测试
查询API,缓冲流读写方法与基本的流是一致的,我们通过复制大文件(375MB),测试它的效率。
//方法1:使用FileInputStream\FileOutputStream实现非文本文件的复制
public void copyFileWithFileStream(String srcPath,String destPath){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//1. 造文件-造流
fis = new FileInputStream(new File(srcPath));
fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(destPath));
//2. 复制操作(读、写)
byte[] buffer = new byte[100];
int len;//每次读入到buffer中字节的个数
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("复制成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//3. 关闭资源
try {
if (fos != null)
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if (fis != null)
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
@Test
public void test1(){
String srcPath = "C:\\Users\\shkstart\\Desktop\\01-复习.mp4";
String destPath = "C:\\Users\\shkstart\\Desktop\\01-复习2.mp4";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
copyFileWithFileStream(srcPath,destPath);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("花费的时间为:" + (end - start));//7677毫秒
}
//方法2:使用BufferedInputStream\BufferedOuputStream实现非文本文件的复制
public void copyFileWithBufferedStream(String srcPath,String destPath){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//1. 造文件
File srcFile = new File(srcPath);
File destFile = new File(destPath);
//2. 造流
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//3. 读写操作
int len;
byte[] buffer = new byte[100];
while ((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
bos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("复制成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4. 关闭资源(如果有多个流,我们需要先关闭外面的流,再关闭内部的流)
try {
if (bos != null)
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if (bis != null)
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
@Test
public void test2(){
String srcPath = "C:\\Users\\shkstart\\Desktop\\01-复习.mp4";
String destPath = "C:\\Users\\shkstart\\Desktop\\01-复习2.mp4";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
copyFileWithBufferedStream(srcPath,destPath);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("花费的时间为:" + (end - start));//415毫秒
}
3. 字符缓冲流特有方法
字符缓冲流的基本方法与普通字符流调用方式一致,不再阐述,我们来看它们具备的特有方法。
-
BufferedReader:
public String readLine(): 读一行文字。 -
BufferedWriter:
public void newLine(): 写一行行分隔符,由系统属性定义符号。
public class BufferedIOLine {
@Test
public void testReadLine()throws IOException {
// 创建流对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("in.txt"));
// 定义字符串,保存读取的一行文字
String line;
// 循环读取,读取到最后返回null
while ((line = br.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
// 释放资源
br.close();
}
@Test
public void testNewLine()throws IOException{
// 创建流对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("out.txt"));
// 写出数据
bw.write("尚");
// 写出换行
bw.newLine();
bw.write("硅");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("谷");
bw.newLine();
// 释放资源
bw.close();
}
}
说明:
涉及到嵌套的多个流时,如果都显式关闭的话,需要先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流
其实在开发中,只需要关闭最外层的流即可,因为在关闭外层流时,内层的流也会被关闭。
4. 练习
**练习1:**分别使用节点流:FileInputStream、FileOutputStream和缓冲流:BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream实现文本文件/图片/视频文件的复制。并比较二者在数据复制方面的效率。
练习2:
姓氏统计:一个文本文件中存储着北京所有高校在校生的姓名,格式如下:
每行一个名字,姓与名以空格分隔:
张 三
李 四
王 小五
现在想统计所有的姓氏在文件中出现的次数
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("e:/name.txt")));
String value = null; // 临时接收文件中的字符串变量
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
flag:
while ((value = br.readLine()) != null) { // 开始读取文件中的字符
char[] c = value.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
if (c[i] != ' ') {
buffer.append(String.valueOf(c[i]));
} else {
if (map.containsKey(buffer.toString())) {
int count = map.get(buffer.toString());
map.put(buffer.toString(), count + 1);
} else {
map.put(buffer.toString(), 1);
}
buffer.delete(0, buffer.length());
continue flag;
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (br != null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> set = map.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> it = set.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> end = (Map.Entry<String, Integer>) it.next();
System.out.println(end);
}
}