1 标准输入、输出流
-
System.in和System.out分别代表了系统标准的输入和输出设备
-
默认输入设备是:键盘,输出设备是:显示器
-
System.in的类型是InputStream
-
System.out的类型是PrintStream,其是OutputStream的子类FilterOutputStream 的子类
-
重定向:通过System类的setIn,setOut方法对默认设备进行改变。
-
public static void setIn(InputStream in)
-
public static void setOut(PrintStream out)
-
举例:
从键盘输入字符串,要求将读取到的整行字符串转成大写输出。然后继续进行输入操作,直至当输入“e”或者“exit”时,退出程序。
System.out.println("请输入信息(退出输入e或exit):");
// 把"标准"输入流(键盘输入)这个字节流包装成字符流,再包装成缓冲流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s = null;
try {
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { // 读取用户输入的一行数据 --> 阻塞程序
if ("e".equalsIgnoreCase(s) || "exit".equalsIgnoreCase(s)) {
System.out.println("安全退出!!");
break;
}
// 将读取到的整行字符串转成大写输出
System.out.println("-->:" + s.toUpperCase());
System.out.println("继续输入信息");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (br != null) {
br.close(); // 关闭过滤流时,会自动关闭它包装的底层节点流
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
拓展:
System类中有三个常量对象:System.out、System.in、System.err
查看System类中这三个常量对象的声明:
public final static InputStream in = null;
public final static PrintStream out = null;
public final static PrintStream err = null;
奇怪的是,
-
这三个常量对象有final声明,但是却初始化为null。final声明的常量一旦赋值就不能修改,那么null不会空指针异常吗?
-
这三个常量对象为什么要小写?final声明的常量按照命名规范不是应该大写吗?
-
这三个常量的对象有set方法?final声明的常量不是不能修改值吗?set方法是如何修改它们的值的?
final声明的常量,表示在Java的语法体系中它们的值是不能修改的,而这三个常量对象的值是由C/C++等系统函数进行初始化和修改值的,所以它们故意没有用大写,也有set方法。
public static void setOut(PrintStream out) {
checkIO();
setOut0(out);
}
public static void setErr(PrintStream err) {
checkIO();
setErr0(err);
}
public static void setIn(InputStream in) {
checkIO();
setIn0(in);
}
private static void checkIO() {
SecurityManager sm = getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("setIO"));
}
}
private static native void setIn0(InputStream in);
private static native void setOut0(PrintStream out);
private static native void setErr0(PrintStream err);
练习:
Create a program named MyInput.java: Contain the methods for reading int, double, float, boolean, short, byte and String values from the keyboard.
package com.atguigu.java;
// MyInput.java: Contain the methods for reading int, double, float, boolean, short, byte and
// string values from the keyboard
import java.io.*;
public class MyInput {
// Read a string from the keyboard
public static String readString() {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// Declare and initialize the string
String string = "";
// Get the string from the keyboard
try {
string = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
}
// Return the string obtained from the keyboard
return string;
}
// Read an int value from the keyboard
public static int readInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(readString());
}
// Read a double value from the keyboard
public static double readDouble() {
return Double.parseDouble(readString());
}
// Read a byte value from the keyboard
public static double readByte() {
return Byte.parseByte(readString());
}
// Read a short value from the keyboard
public static double readShort() {
return Short.parseShort(readString());
}
// Read a long value from the keyboard
public static double readLong() {
return Long.parseLong(readString());
}
// Read a float value from the keyboard
public static double readFloat() {
return Float.parseFloat(readString());
}
}
2. 打印流
-
实现将基本数据类型的数据格式转化为字符串输出。
-
打印流:
PrintStream和PrintWriter-
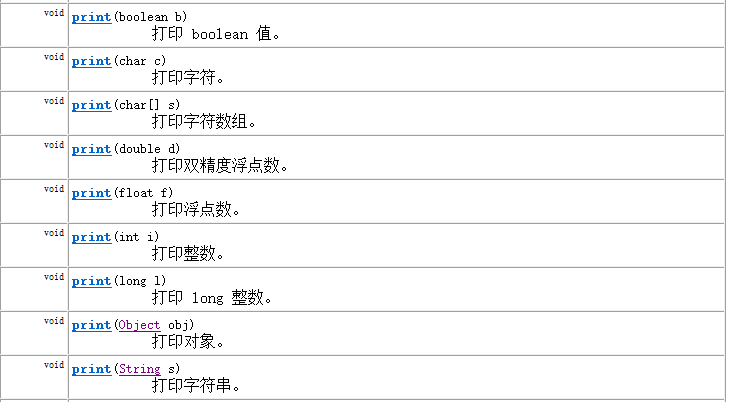
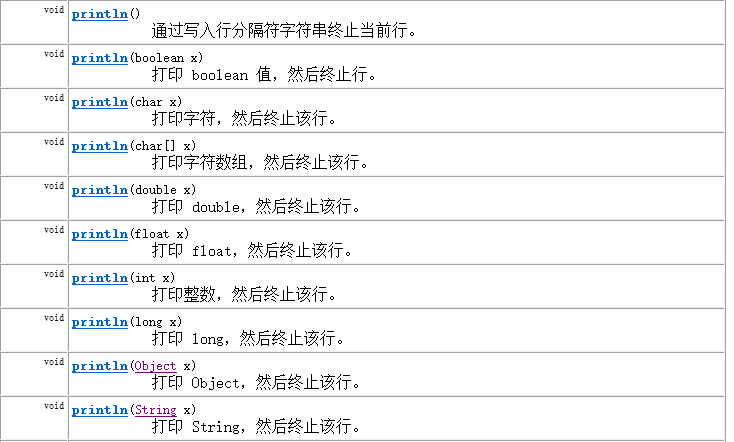
提供了一系列重载的print()和println()方法,用于多种数据类型的输出


-
PrintStream和PrintWriter的输出不会抛出IOException异常
-
PrintStream和PrintWriter有自动flush功能
-
PrintStream 打印的所有字符都使用平台的默认字符编码转换为字节。在需要写入字符而不是写入字节的情况下,应该使用 PrintWriter 类。
-
System.out返回的是PrintStream的实例
-
-
构造器
-
PrintStream(File file) :创建具有指定文件且不带自动行刷新的新打印流。
-
PrintStream(File file, String csn):创建具有指定文件名称和字符集且不带自动行刷新的新打印流。
-
PrintStream(OutputStream out) :创建新的打印流。
-
PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush):创建新的打印流。 autoFlush如果为 true,则每当写入 byte 数组、调用其中一个 println 方法或写入换行符或字节 (‘\n’) 时都会刷新输出缓冲区。
-
PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, String encoding) :创建新的打印流。
-
PrintStream(String fileName):创建具有指定文件名称且不带自动行刷新的新打印流。
-
PrintStream(String fileName, String csn) :创建具有指定文件名称和字符集且不带自动行刷新的新打印流。
-
-
代码举例1
package com.atguigu.systemio;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class TestPrintStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("io.txt");
ps.println("hello");
ps.println(1);
ps.println(1.5);
ps.close();
}
}
- 代码举例2
PrintStream ps = null;
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\IO\\text.txt"));
// 创建打印输出流,设置为自动刷新模式(写入换行符或字节 '\n' 时都会刷新输出缓冲区)
ps = new PrintStream(fos, true);
if (ps != null) {// 把标准输出流(控制台输出)改成文件
System.setOut(ps);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 255; i++) { // 输出ASCII字符
System.out.print((char) i);
if (i % 50 == 0) { // 每50个数据一行
System.out.println(); // 换行
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
}
- 代码举例3:自定义一个日志工具
/*
日志工具
*/
public class Logger {
/*
记录日志的方法。
*/
public static void log(String msg) {
try {
// 指向一个日志文件
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("log.txt", true));
// 改变输出方向
System.setOut(out);
// 日期当前时间
Date nowTime = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS");
String strTime = sdf.format(nowTime);
System.out.println(strTime + ": " + msg);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class LogTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试工具类是否好用
Logger.log("调用了System类的gc()方法,建议启动垃圾回收");
Logger.log("调用了TeamView的addMember()方法");
Logger.log("用户尝试进行登录,验证失败");
}
}
3. Scanner类
构造方法
-
Scanner(File source) :构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定文件扫描的。
-
Scanner(File source, String charsetName) :构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定文件扫描的。
-
Scanner(InputStream source) :构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定的输入流扫描的。
-
Scanner(InputStream source, String charsetName) :构造一个新的 Scanner,它生成的值是从指定的输入流扫描的。
常用方法:
-
boolean hasNextXxx(): 如果通过使用nextXxx()方法,此扫描器输入信息中的下一个标记可以解释为默认基数中的一个 Xxx 值,则返回 true。
-
Xxx nextXxx(): 将输入信息的下一个标记扫描为一个Xxx
package com.atguigu.systemio;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestScanner {
@Test
public void test01() throws IOException {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("1.txt");
while(true){
System.out.print("请输入一个单词:");
String str = input.nextLine();
if("stop".equals(str)){
break;
}
ps.println(str);
}
input.close();
ps.close();
}
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
Scanner input = new Scanner(new FileInputStream("1.txt"));
while(input.hasNextLine()){
String str = input.nextLine();
System.out.println(str);
}
input.close();
}
}